LINSEED;
Are the benefits really worth it?

Wondering why Linseed among many other?
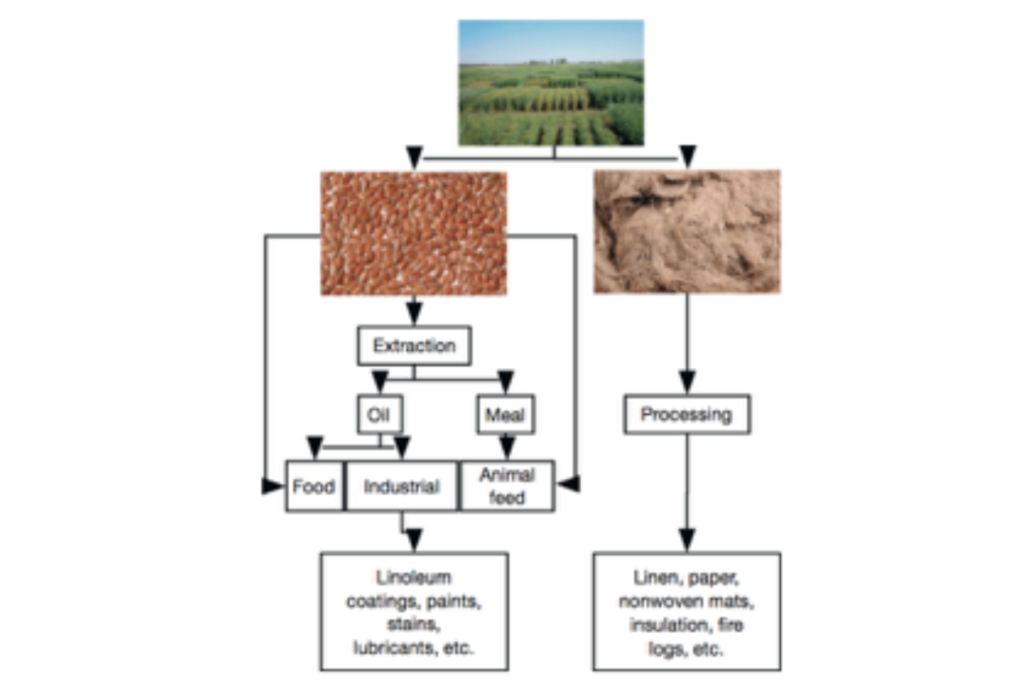
Linseed has its uniqueness in comparison to other oilseed crops. Though it is a minor oilseed crop, but has a unique fatty acid profile. That suggests that moderate consumption of Linseed attributes to health benefits in humans (1). Linseed or also known as Flax is versatile in nature. Not only the seed, its Stem fiber is used in processing high quality linen. Wholeseed can be used in food industry and animal feed as well.
Health Benefits;
We know the importance of the omega 3 fatty acids in human health. Omega 3 is an essential fatty acids but human body cannot make them. Linseed turns out to be a promising source of omega 3 whose health benefits include
• Reduction of blood pressure, blood triglycerides, inflammation, and the incidence of cardio vascular disease.
• Recently, Health Canada has granted a health claim regarding the effectiveness of ground flaxseed on lowering cholesterol allowing health claims such as the following to be made on flaxseed labels: 16 g or 2 tablespoons of ground flaxseed supplies 40% of the daily amount shown to help lower cholesterol.
• Linseed comprises of both soluble and insoluble fibre.
• Lignan, the phytoestrogen is a part of dietary component which is associated with the reduced risk of hormone sensitive cancers such as colon, breast and prostrate (5).
What Nutritional Value it has?
• Proteins, has amino acid profile comparable to soya bean.
• Lipids, its the richest plant source of omega 3 fatty acids, α- linolenic acid is the major fatty acid ranging from 39.00 to 60.42 %. Provides an excellent ω-6:ω-3 fatty acid ratio of approximately 0.3:1.
• Dietary fibers, are the oldest fibre crop in the world. Its a natural , biodegradable composite exhibiting good mechanical properties and low density.
• Lignans, act as both antioxidants and phytoestrogens. Phytoestrogens can have weak oestrogen activity in animals and humans. Thus, showing promising effects in reducing the cancerous tutors, especially hormone sensitive like breast, endometrium and prostrate. A systematic review suggests Flax demonstrates anti proliferative effects in breast tissue of women at risk of breast cancer (3).
• Minerals, has higher potassium than the recommended source such as banana. Also, a 30gm of seed content contains 7%-30% of RDA of minerals like calcium, magnesium and phosphorous. Apart from being a superfood its of tremendous use as raw material for the high-quality paper industry for the use of printed banknotes and rolling paper for cigarettes and tea bags (2).

Flax; An Ayurvedic Medicine/ Historical Medicine
YES! Ayurveda one of the most ancient and yet alive tradition in India and many other countries also believes that the flaxseed oil helps fight mental and physical fatigue and controls raging process. It can be consumed in as easy ways such as flaxseed tea, flaxseed drink, flaxseed flour and the benefits are numerous such as tea is useful against bronchitis, cough, against dyspnoea. The drink helps relieve constipation and the flour has endless benefits like it cures inflammation of intestine and pain in the abdomen, strengthens
Traditonal and medicinal
uses….
Research suggests significant reductions in both SBP and DBP following supplementation with various flaxseed products. Another meta analysis suggests beneficial potential of flaxseed consumption, as a whole seed for more than 12 weeks, to reduce diastolic blood pressure (4). For recipes wit flaxseed and oil refer to the link below; htttp://food.ndtv.com/food-drinks/how-t-eat-flaxseeds
References
1. Cloutier S. Linseed: Overview – Encyclopedia of Food Grains (Second Edition), 259-264 [Internet]. Ac.els-cdn.com. 2016 [cited 15 September 2017].
2. Goyal A, Sharma V, Upadhyay N, Siha M, Gill S. J Food Sci Technol (September 2014) 51(9): 1633–1653 DOI 10.1007/s13197-013-1247-9 [Internet]. 2014 [cited 15 September 2017].
Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4152533/pdf/ 13197_2013_Article_1247.pdf
3. Flower, G, Fritz H, Balneaves L, Verma S, Skidmore B, Fernandes R et al. Flax and Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. Integrative Cancer Therapies [Internet]. 2014 [cited 17 September 2017];Vol. 13(3):181–192.
Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1534735413502076
4. Khalesi S, Schubert M, Irwin C. Flaxseed Consumption May Reduce Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis of Controlled Trials1–3. The Journal of Nutrition Nutrition and Disease [Internet]. 2015 [cited 14 September 2017];vol. 145(4): 758-765.
Available from: http://jn.nutrition.org/content/145/4/758.full.pdf+html
5. Zukab M, Richter D, Szopaa J, Matula J. Linseed, the multipurpose plant [Internet]. Sciencedirect.com. 2015 [cited 17 September 2017].
Available from: http:// www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926669015300832
