What are FODMAPS?

FODMAP is a short form for Fermentable-Oligosaccharides-disaccharides- Monosaccharides and polyols. These are a specific (short chain) type of carbohydrates, that some people are unable to digest and absorb efficiently. These carbohydrates reach the large intestine without being efficiently digested and act as a fuel for the bacteria residing in the large intestine, producing hydrogen gas. As a result, it leads to symptoms such as gas, bloating, and diarrhea, stomach pain in sensitive individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Foods containing high FODMAPS can be categorized as follows-
Oligosaccharides– Made up of 3-10 simple sugars and commonly found in fruits, vegetable, grains and legumes.
Fructose– are monosaccharides, most commonly found sugar in fruits, vegetables, honey, sugar sweetened-beverages and foods and high fructose corn syrup.
Disaccharides- these are compound sugars containing two monosaccharide (lactose, maltose and sucrose) found in dairy products such as milk, yogurt and soft cheese.
Polyols- these are the sugar alcohols found in certain fruits and vegetables And sugar- free sweeteners. Some FDA approved polyols are
erythritol, hydrogenated starch hydrolysates, isomalt, lactitol, maltitol, mannitol, sorbitol, and xylitol (1)
Examples of High FODMAP foods-
Fruits & Vegetables: apples, pears, mangoes, cherries, figs, nashi pears, pears, watermelon and dried fruit; artichoke, garlic, leek, onion, cauliflower, mushrooms.
Dairy foods: ice cream, most yogurts, soft and fresh cheeses (cottage cheese, ricotta, etc.), sour cream, whey protein supplements;
Grains: wheat, whole-meal bread, rye bread, muesli containing wheat, wheat pasta and rye crispbread;
Pulses & Legumes: red kidney beans, split peas, falafels and baked beans;
Sweeteners: agave nectar, fructose, high fructose corn syrup, honey, malt extract, maltitol, mannitol, molasses, sorbitol, xylitol;(2)
Examples of Low FODMAP foods-
Fruits & Vegetables: blueberries, cantaloupe, kiwi, lemon, oranges, pineapple (raw); carrots, chives, eggplant, green beans, kale, potato.
Dairy foods: butter, cheeses (2 oz. or less): cottage, feta, ricotta, mozzarella, Swiss; lactose-free milk, rice/oat milk, tofu (firm), tempeh
Nuts and Seeds: Brazil nuts, chestnuts, chia seeds, flax seeds, macadamias, peanuts, pecan halves, pine nuts, pumpkin seeds, walnut halves
Fats and oil: almond oil, avocado oil, butter/ghee, coconut milk, coconut oil, olives, olive oil (extra virgin), rice bran oil, safflower, sesame oil, sunflower oil, walnut oil (3)

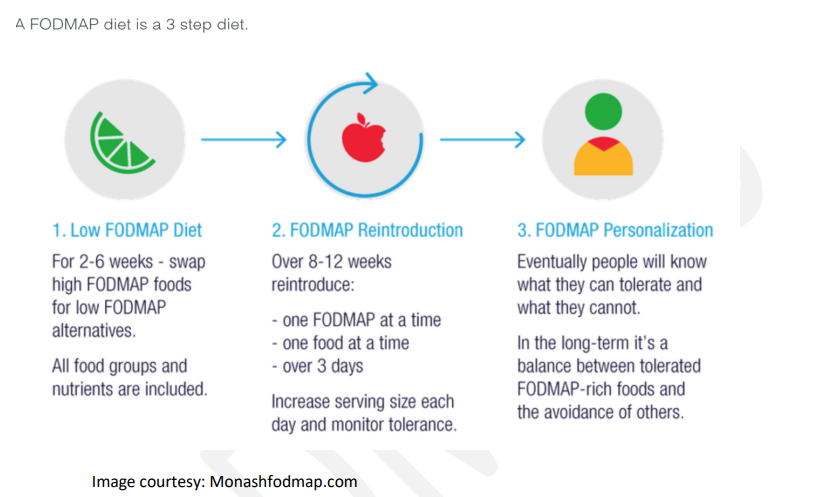
How to implement the Low-FODMAP Diet?
• Organize your kitchen by identifying foods that should be eliminated, and stocking up on low-FODMAP foods.
References
1. A systematic review of the effects of Polyols on GI health and irritable bowel syndrome.
Adrienne Lenhart 1, William D Chey
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5508768/
2. BANT FODMAP food & nutrition guide.
3. IFM resource.
